The spreadsheet can be open when importing the results back into Revit. On the Add-Ins ribbon, select ExcelLink – Update Revit From Excel.
In the drop down menu in the Update Revit From Excel window, select the spreadsheet file to update from. Double click on the parameter set Spaces to view the changes made to the spreadsheet.
Review the changes made in the Excel spreadsheet, and deselect any that should not be carried over to Revit and click Apply Changes.
The data will now be assigned to the parameters in the space elements, which will show up in space schedules, such as the space airflow schedule, and also in the properties for the spaces. This information can then be used in the design process, for example to highlight spaces where the actual supply airflow out of the air terminals within the space do not meet the required airflow for the space calculated by IES.
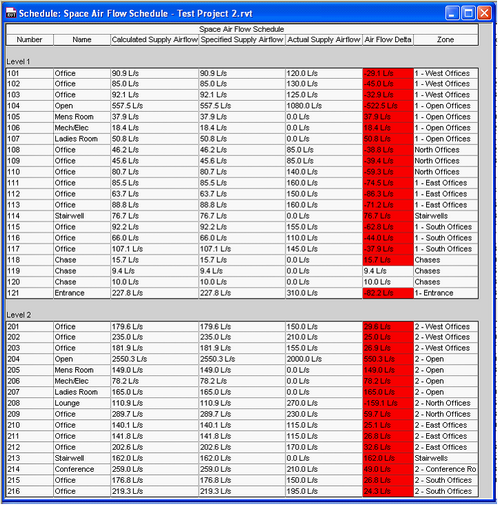
Space Schedule before update from Excel
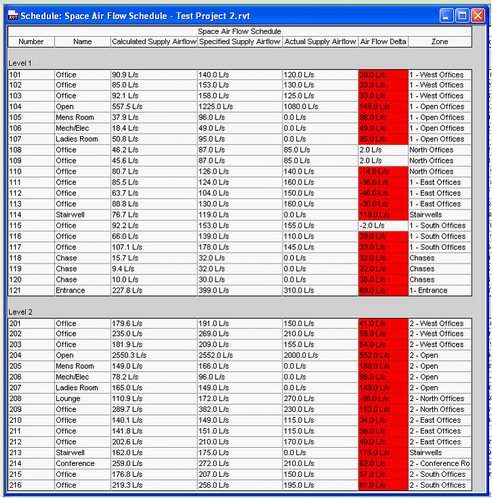
Space schedule after update from Excel - Note changes to the Air Flow data
Above, before and after importing data from Excel into Revit. The specified Supply Airflow is the value from IES, while Calculated Supply Airflow (and specified before importing IES data) is the airflow requirements calculated by the Camel loads engine built into Revit MEP 2010/2011.
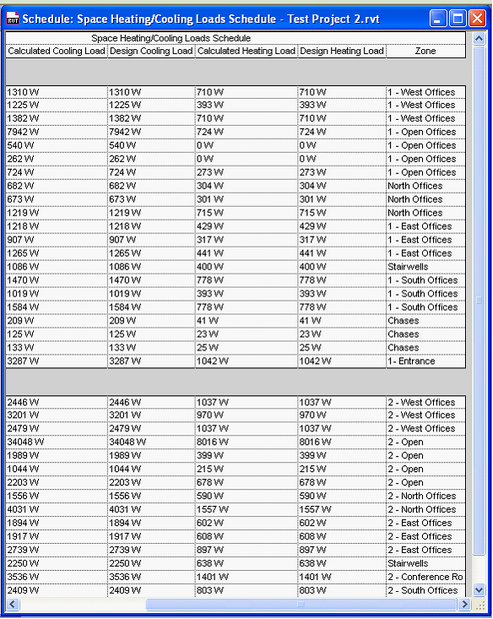
Space Heating/Cooling loads schedule - Before
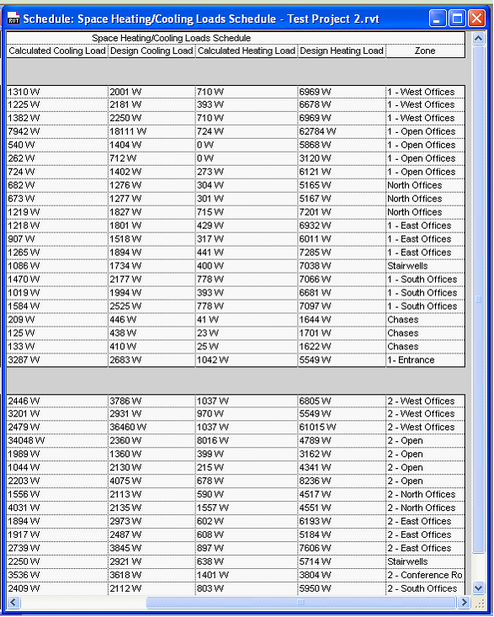
Space Heating/Cooling loads schedule - After
Above, before and after importing data from Excel into Revit. The specified Design Heating Load/ Design Cooling Load is the value from IES, while Calculated Heating Load/Calculated Cooling Load (and specified before importing IES data) are the loads results calculated by the Camel loads engine built into Revit MEP 2010/2011.
(Note: the large discrepancy between the numbers calculated by the inbuilt Camel engine and IES above is due to the location for both tests being different, Sydney, Australia versus Zurich, Switzerland. With the same location used in both software, the results are still differ significantly however, with the Camel loads and airflows around half those calculated by IES, although not always by the same factor.)
Direct link to this topic:
© 2015 Arup